Difference between revisions of "RFID"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | '''RFID''' ('''R'''adio '''F'''requency '''ID'''entification) allows identification and | + | '''RFID''' ('''R'''adio '''F'''requency '''ID'''entification) allows identification and localization of objects and/or living beings. It requires a '''transponder''' and a '''reading device'''. The transponder is nothing more than a chip being fixed to the object or being embedded into it. This chip puts out a code as soon as it passes the reading device at a certain distance. This code will be interpreted by a software and all information can be generated in clear words. |
| − | In order to enlarge the reading distance between transponder and reading device, a little antenna | + | In order to enlarge the reading distance between transponder and reading device, a little antenna structure can be added to the chip. This might be embedded to the chip itself or externally designed.<br><br> |
<table border="0" cellspacing="60" cellpadding="5" valign="top"><tr><td>[[Image:rfidtag.jpg]]<br>An RFID chip with antenna structure<br>on a ground plane.<br><small>Image source:[http://www.murata.com/new/news_release/2008/pdf/nr0851e.pdf muRata]</small><br></td><td>[[Image:rfid__radio.GIF]]<br>Lateral embedding of an RFID chip with<br>connection to the antenna by buried vias<br><small>see [http://www.pcb-pool.com/ppuk/info_pcbpool_rfid.html Magic-PCB®]</small><br></td></tr></table><br> | <table border="0" cellspacing="60" cellpadding="5" valign="top"><tr><td>[[Image:rfidtag.jpg]]<br>An RFID chip with antenna structure<br>on a ground plane.<br><small>Image source:[http://www.murata.com/new/news_release/2008/pdf/nr0851e.pdf muRata]</small><br></td><td>[[Image:rfid__radio.GIF]]<br>Lateral embedding of an RFID chip with<br>connection to the antenna by buried vias<br><small>see [http://www.pcb-pool.com/ppuk/info_pcbpool_rfid.html Magic-PCB®]</small><br></td></tr></table><br> | ||
| − | '''Important''': The RFID chip has nothing to do with the electrical logic of the board. It is | + | '''Important''': The RFID chip has nothing to do with the electrical logic of the board. It is electronically completely independent.<br>The energy required is supplied by the magnetic field of the reading device.<br><br> |
| − | The combination of chip and antenna might be very small and e.g. can be designed on foil. So it is very easy to fix such an RFID tag to any object. Why shouldn't a PCB be furnished with such a tag for identification or | + | The combination of chip and antenna might be very small and e.g. can be designed on foil. So it is very easy to fix such an RFID tag to any object. Why shouldn't a PCB be furnished with such a tag for identification or localization at any step of further process chain control? At any time e.g. during the process of assembly the board individually can be located and identified. |
The PCB house '''PCB-POOL®''' offers '''[http://www.pcb-pool.com/ppde/info_pcbpool_rfid.html Magic PCB®]''', a technique to embed an RFID tag laterally to the edge of a board and connect it to an antenna from the inside. Then it gets resin cast ans thus irreversibly is fixed to the PCB. From the outside only the antenna structure can be seen. | The PCB house '''PCB-POOL®''' offers '''[http://www.pcb-pool.com/ppde/info_pcbpool_rfid.html Magic PCB®]''', a technique to embed an RFID tag laterally to the edge of a board and connect it to an antenna from the inside. Then it gets resin cast ans thus irreversibly is fixed to the PCB. From the outside only the antenna structure can be seen. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
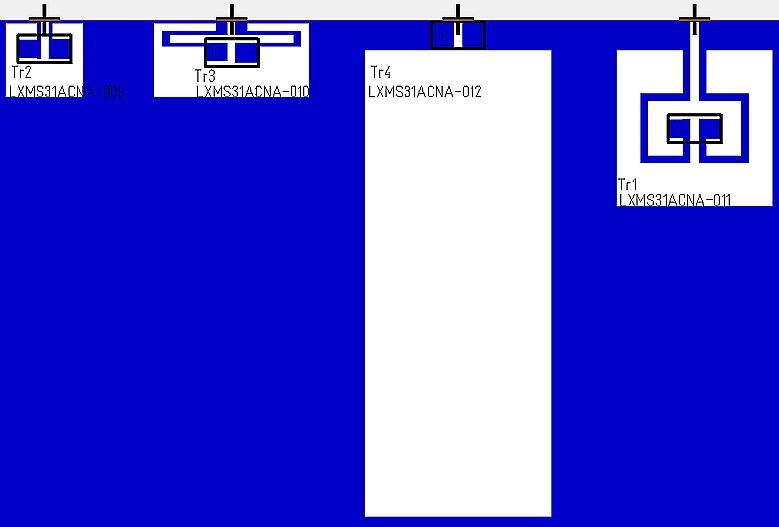
| − | In TARGET 3001! there are various antenna geometries available. Load them to your layout like a component from the database and embed them to your | + | In TARGET 3001! there are various antenna geometries available. Load them to your layout like a component from the database and embed them to your ground plane (if there is one). <br><br> |
Revision as of 15:22, 11 April 2013
RFID (Radio Frequency IDentification) allows identification and localization of objects and/or living beings. It requires a transponder and a reading device. The transponder is nothing more than a chip being fixed to the object or being embedded into it. This chip puts out a code as soon as it passes the reading device at a certain distance. This code will be interpreted by a software and all information can be generated in clear words.
In order to enlarge the reading distance between transponder and reading device, a little antenna structure can be added to the chip. This might be embedded to the chip itself or externally designed.
 An RFID chip with antenna structure on a ground plane. Image source:muRata |  Lateral embedding of an RFID chip with connection to the antenna by buried vias see Magic-PCB® |
Important: The RFID chip has nothing to do with the electrical logic of the board. It is electronically completely independent.
The energy required is supplied by the magnetic field of the reading device.
The combination of chip and antenna might be very small and e.g. can be designed on foil. So it is very easy to fix such an RFID tag to any object. Why shouldn't a PCB be furnished with such a tag for identification or localization at any step of further process chain control? At any time e.g. during the process of assembly the board individually can be located and identified.
The PCB house PCB-POOL® offers Magic PCB®, a technique to embed an RFID tag laterally to the edge of a board and connect it to an antenna from the inside. Then it gets resin cast ans thus irreversibly is fixed to the PCB. From the outside only the antenna structure can be seen.

This 2min film illustrates the
layout process in TARGET 3001!
In TARGET 3001! there are various antenna geometries available. Load them to your layout like a component from the database and embed them to your ground plane (if there is one).