Polygone de signal : Différence entre versions
(→What you can do) |
(→Comment faire) |
||
| Ligne 22 : | Ligne 22 : | ||
| − | <b> | + | <b>Couche:</b> Un polygone avec assignation de signal ne peut être créé que sur une couche de cuivre. Les couches de cuivre utilisées dans votre projet peuvent être sélectionnées dans la liste déroulante. Sélectionnez la couche de cuivre sur laquelle votre polygone apparaîtra plus tard (face soudure, face composant, couche interne). <br><br> |
| − | <b>Signal:</b> | + | <b>Signal:</b> Sélectionnez le signal à attribuer au polygone. À ce stade, vous ne pouvez attribuer qu'un seul signal à un seul polygone. La création d'un [[Couplage en étoil (GND)]] est un sujet distinct.<br><br> |
| − | <b> | + | <b>Largeur de ligne:</b> En mots faciles, la largeur de la piste est l'épaisseur du stylo que vous utilisez pour remplir le polygone avec couleur. Sonne un peu enfantin, mais en ce qui concerne la technique de production, c'est la meilleure façon de comparer. En Gerber, un stylo photo suit les lignes sur un panneau photosensible avec une ouverture selon la largeur de la piste. Plus la pointe du stylo est nette, plus on peut construire des structures plus filigranées. Discutez de la plus petite valeur avec votre fabricant-PCB. Ici en Europe, la valeur minimale de 0,15 mm est commune.<br><br> |
| − | + | L'image suivante montre le polygone avec une petite flèche de l'encoche. La raison en est une largeur de piste trop large. Le stylo ne peut pas passer par le point le plus étroit.<br><br> | |
| − | [[image:signalpolygone_gap.jpg| | + | [[image:signalpolygone_gap.jpg|Largeur de piste trop large]]<br>La largeur de la piste est trop grande pour fermer la zone à cet endroit.<br><br> |
Referring to the track width set here the DesignRuleCheck later checks whether the minimum track width od a connection is fulfilled. The track width must also be seen in combination with the "Grid spacing". A gridded ground plane in consists of a net-structure made of orthogonal intersecting lines. The width of this lines you also define here. You can only enter one value for the track width here. The net structure (= ground plane in lines) always has a square mesh structure.<br><br> | Referring to the track width set here the DesignRuleCheck later checks whether the minimum track width od a connection is fulfilled. The track width must also be seen in combination with the "Grid spacing". A gridded ground plane in consists of a net-structure made of orthogonal intersecting lines. The width of this lines you also define here. You can only enter one value for the track width here. The net structure (= ground plane in lines) always has a square mesh structure.<br><br> | ||
Version du 27 juillet 2017 à 09:24
![]()
L'icône se trouve parmi les fonctions de dessin.
Généralités
Tout polygone rempli sur une couche de cuivre peut être muni d'un signal. Il peut être manipulé comme un plan de masse séparé. Il peut être fourni individuellement avec des attributs. Sur une couche de cuivre, plusieurs polygones avec des signaux différents peuvent être dessinés.
Vous pouvez accéder à ce mode:
- par touche de clavier [6],
- par élément du menu "6 Dessiner un polygone de masse" dans menu "Éléments"
- par l'icône
 entre des fonctions de dessin
entre des fonctions de dessin 
Comment faire
Définissez les coins du polygone par M1. Vous pouvez fermer le polygone automatiquement par "Retour" lors du dessin du dernier segment. M2 fait de même que vous finissez la ligne exactement sur le point de départ du polygone. Immédiatement, le dialogue pour l'édition du polygone de signal s'ouvre.
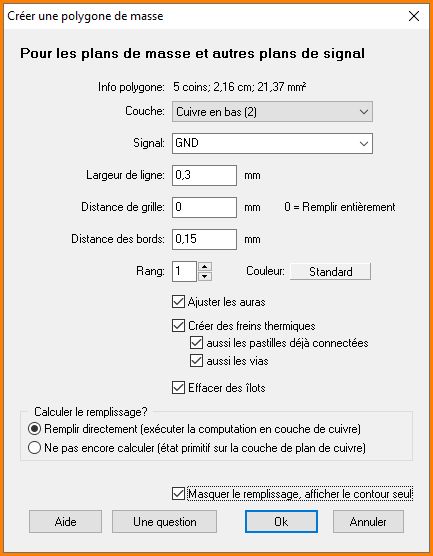
Le dialogue pour l'édition du polygone de signal
Couche: Un polygone avec assignation de signal ne peut être créé que sur une couche de cuivre. Les couches de cuivre utilisées dans votre projet peuvent être sélectionnées dans la liste déroulante. Sélectionnez la couche de cuivre sur laquelle votre polygone apparaîtra plus tard (face soudure, face composant, couche interne).
Signal: Sélectionnez le signal à attribuer au polygone. À ce stade, vous ne pouvez attribuer qu'un seul signal à un seul polygone. La création d'un Couplage en étoil (GND) est un sujet distinct.
Largeur de ligne: En mots faciles, la largeur de la piste est l'épaisseur du stylo que vous utilisez pour remplir le polygone avec couleur. Sonne un peu enfantin, mais en ce qui concerne la technique de production, c'est la meilleure façon de comparer. En Gerber, un stylo photo suit les lignes sur un panneau photosensible avec une ouverture selon la largeur de la piste. Plus la pointe du stylo est nette, plus on peut construire des structures plus filigranées. Discutez de la plus petite valeur avec votre fabricant-PCB. Ici en Europe, la valeur minimale de 0,15 mm est commune.
L'image suivante montre le polygone avec une petite flèche de l'encoche. La raison en est une largeur de piste trop large. Le stylo ne peut pas passer par le point le plus étroit.
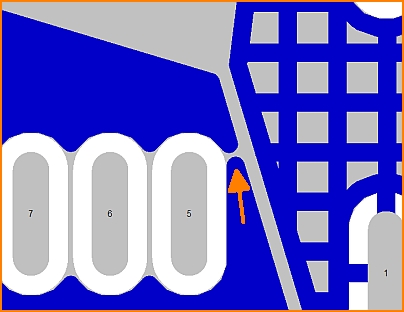
La largeur de la piste est trop grande pour fermer la zone à cet endroit.
Referring to the track width set here the DesignRuleCheck later checks whether the minimum track width od a connection is fulfilled. The track width must also be seen in combination with the "Grid spacing". A gridded ground plane in consists of a net-structure made of orthogonal intersecting lines. The width of this lines you also define here. You can only enter one value for the track width here. The net structure (= ground plane in lines) always has a square mesh structure.
Grid spacing: A ground plane in lines offers production advantages in galvanization and also is preferable in respect to electromegnetic performance of the signal. In addition to the track width you can define the distance of the mesh.
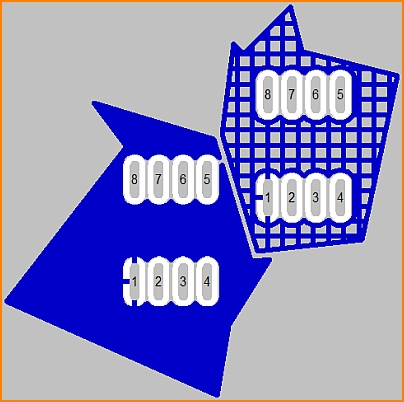
Copper top: Ground plane in lines (to the right). Track width: 0.3mm, Grid spacing: 0.5mm
PCB edge spacing: It is helpful to have a little spacing between ground plane and cutting edge of the PCB. It can avoid a short circuit by just touching the board by any other object. Also a crosstalk of the signal can be avoided. Cutting edge is middle of the PCB outline.
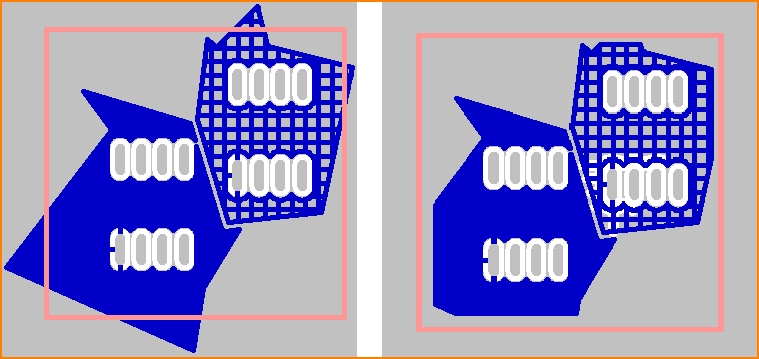
Distance to the edge: left without, right with "stand back" from the edge of the board. In the image to the right the left polygon shows a PCB edge spacing of 0.8mm, the one right beside shows a spacing to the edge of 0.4mm.
Rank: Polygons can overlap, they even can interlace - sure they never should touch each other. Which of the polygons should dominate the other (taking away some of the others shape) can be defined by its rank. The higher the cipher of the rank of a polygon is, the more dominant it is. A polygon with rank 2 dominates a polygon having only rank 1. This means the one with rank 2 takes away the overlapping from the one with rank 1 and so on. There are 99 ranks possible.
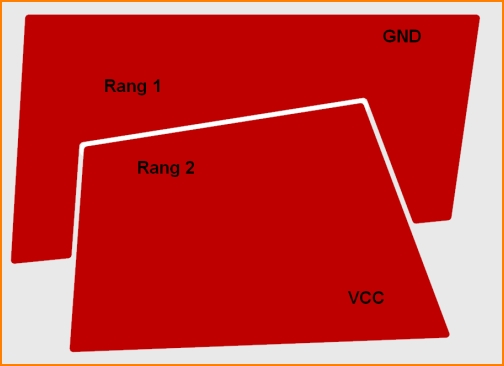
Face soudure: Entrelacement de polygones avec différents signaux et rangs différents
Create thermal pads: A thermal pad is a connecting pad which is not completely embedded to the plane but it connects only by small ligaments. It effects reduced heat dissipation into the plane. This supports good connection of solder agens and copper pad. Those ligaments can look crosswise, y-shaped or straight. Also see Thermal Pads.
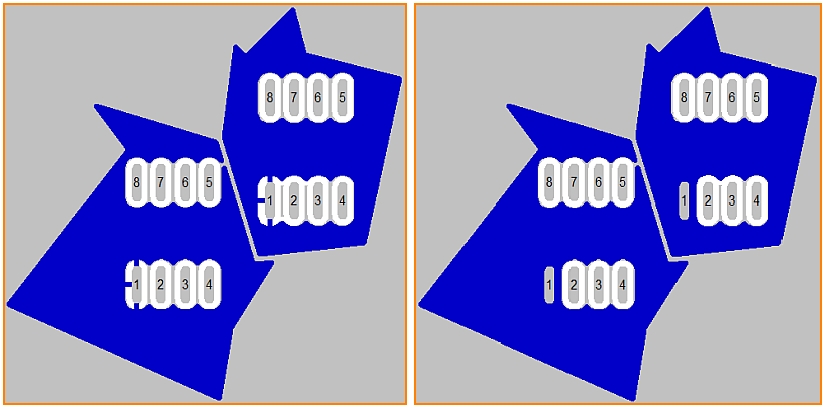
The pads numbered 1 of the two components being located to two polygons. Left with thermal pads, right without.
Delete islands: A not connected piece of a signal polygon is called an "Island". They are also called "Orphans". They dont have any purpose and mostly make trouble. So they should be removed. TARGET does this automatically if you tick the box. A ground plane gets connected by a pad of a component, A via having an aura of 0 upon this layer or a piece of track running through the polygon plane and having aura =0. Always the signal name (the signal) must be identical.
Fill directly : The polygon immediately gets created wit all interactions to all other elements. This process can take some seconds in bigger projects. Therefore you can switch it off here by unticking the box. By default the box is ticked.

